Introduction to Commodity Trading
Commodity trading involves much of what we'd consider the necessities of life. Hence the name, commodities. This includes everything from agricultural products like beef, grain, corn, and soy, to other physical products like oil, natural gas, and gold. As investors seek to diversify their portfolios, commodity trading, like many other segments of the market, has been consolidated into indexes and funds for easier access to diversification.
Successfully investing in commodities demands not only a keen understanding of market dynamics but also access to reliable tools and indices. In this exploration, we take a look at a key player in the commodity trading landscape—the Goldman Sachs Commodity Index (GSCI).
Read on as we unveil the secrets behind successful commodity trading, delving into the intricacies of the GSCI, analyzing commodity market trends, exploring trading strategies, and dissecting market forecasts.
What is the Goldman Sachs Commodity Index (GSCI)?
The Goldman Sachs Commodity Index, commonly known as GSCI, is a leading benchmark for measuring the performance of commodity investments. Established by Goldman Sachs in 1991, the index tracks the price movements of various commodities across sectors like energy, agriculture, industrial metals, and precious metals.
Components of the GSCI
As a "long-only" fund, the GSCI is comprised of 24 exchange-traded futures contracts. This covers at least 5 different sectors of commodities (industrial metals, energy, precious metals, grains & oilseeds, and livestock). Each is assigned a specific weight based on its economic significance and world production. These weights are periodically adjusted to reflect changes in the market. Liquidity is also a large factor in the relative weight of the commodities in the GSCI
Why is the GSCI important for Commodity Trading?
Standard & Poor's eventually took over the GSCI, which is now called the S&P GSCI. With consistent returns over the years, there are a few reasons why this index is important for commodities and to commodities investors. Here are three reasons to consider:
-
Diversification: The GSCI provides traders with diversified exposure to different commodities, reducing the risk associated with investing in a single commodity.
-
Benchmarking: It serves as a benchmark for evaluating the performance of commodity investments, allowing traders to assess their portfolios against a standardized index.
-
Market Predictions: Analysts often use the GSCI to make predictions about future market trends, providing valuable insights for traders.
Explanation of the S&P GSCI Methodology
The S&P GSCI (Standard & Poor's Goldman Sachs Commodity Index) is a popular commodity index used to track the performance of a broad range of commodities. It provides a way for investors to understand how different commodities, like gold, oil, or agricultural products, are doing in the market as a whole.
Here's a breakdown of the S&P GSCI methodology:
-
Selection of Commodities: The S&P GSCI includes a diverse set of commodities from various sectors, like energy, agriculture, industrial metals, and precious metals. These commodities are chosen based on their economic significance and relevance to global markets.
-
Weighting of Commodities: Each commodity in the index is given a specific "weight" based on its importance in the global economy. This weight represents the proportion of that commodity in the overall index. For example, if oil has a higher weight, its performance will have a larger impact on the index.
-
Regular Adjustment: The index is regularly adjusted to reflect changes in the market. This means that if the importance of a particular commodity increases or decreases, its weight in the index will be adjusted accordingly.
-
Price Changes Matter: The S&P GSCI is a "price return" index, which means it tracks the price changes of commodities over time. If the prices of the included commodities go up, the index value goes up, and if they go down, the index value goes down. The GSCI is a "long-only" ETF.
-
No Influence from Company Size: Unlike stock market indices, the S&P GSCI doesn't consider the size of the companies or the value of their shares. It focuses solely on the prices of the included commodities.
-
Futures Contracts: The S&P GSCI primarily uses futures contracts to track commodity prices. A futures contract is an agreement to buy or sell a commodity at a predetermined price on a future date. The index rolls these contracts as they approach expiration to maintain a continuous representation of commodity prices.
-
Diversification: The S&P GSCI is designed to provide a diversified view of the commodity market. This diversification helps reduce the impact of poor performance in one commodity on the overall index.
-
Global Economic Indicator: Because the index includes commodities from various sectors, it is considered a reflection of global economic trends. Changes in the S&P GSCI can indicate shifts in the overall health of the global economy.
In summary, the S&P GSCI is like a basket that holds a variety of commodities. The value of the basket goes up or down based on how the prices of those commodities change. It's a tool that investors use to understand and track the overall performance of the commodity market.
How to Trade the GSCI?
Trading with the GSCI is much easier now than before the S&P took over. With the inception of ETFs that track the index, it is easier than ever for traders to follow the index. One popular way to gain exposure is through the iShares S&P GSCI Commodity Index ETF: ticker symbol GSG.
Cons of Trading the GSCI
As with some futures contracts, the S&P GSCI rolls its futures contracts. This presents issues with the investing concepts called contango and backwardation. Contango is a situation where a commodity's futures price is higher than the spot price. Backwardation is the opposite of contango, where the current spot price is higher than the futures price.
As David Stein explains, holding a futures contract and rolling it into the future contract can present potential losses if the spot price stays the same. This is known as a negative roll yield.
The only way an oil or Bitcoin ETF will earn a positive return when there is a normal futures curve is if the spot price for oil or Bitcoin when a futures contract expires is higher than the oil or Bitcoin futures price at the time the ETF entered the contract. - David Stein -
It is important to note these things, but also important to know that the S&P GSCI is reweighted and rebalanced annually.

Strategies for Commodity Trading Using the GSCI
While no single strategy is fool-proof, most conventional trading strategies can still be applied to trading commodities, commodity ETFs, and especially the GSCI. As with any trading strategy, it is important to consider your risk. How much of your portfolio are you investing, how much do you expect as a return, and what edge do you have in the market?
Not sure what an edge or a strategy is? We have a whole section of our educational blog devoted to these. Be sure to head over and check these out as you have time!
That being said, here are a handful of simple strategies that you might employ in your commodity trading:
1. Trend Following:
- Traders often use the GSCI to identify and follow trends in commodity prices. By analyzing historical data and the index's performance, they can make informed decisions based on prevailing trends.
2. Diversification:
- The GSCI's diverse composition allows traders to diversify their portfolios, mitigating risks associated with the volatility of individual commodities.
3. Hedging Against Inflation:
- Commodities, as tracked by the GSCI, have historically served as a hedge against inflation. Traders strategically allocate their investments to safeguard against the eroding effects of inflation on currency values.
4. Global Economic Indicators:
- The GSCI reflects global economic trends as commodities are integral to various industries. Traders keen on understanding broader economic indicators often turn to the GSCI for insights.
More Trading Strategies for Commodity Trading
In addition to the broader investment strategies above, we would be remiss to not mention these tried and true techniques for trading any commodity or ETF:
1. Fundamental Analysis:
- Examining the fundamental factors affecting individual commodities, such as crop reports for agricultural products or geopolitical events for oil, provides a deeper understanding of market dynamics.
2. Technical Analysis:
- Utilizing technical indicators and charts helps traders identify patterns and trends, enabling more precise entry and exit points for trades. There is no better place to do this than at TradingSim.com
3. Risk Management:
- Implementing robust risk management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders and diversifying portfolios, safeguards traders against significant losses.
4. Stay Informed:
- Continuous learning and staying abreast of global economic developments, policy changes, and market news are crucial for informed decision-making.
Market Forecasting and Analysis for Commodities
Analyzing Historical Data
To unravel the secrets of successful commodity trading, one must delve into historical data. Analyzing how the GSCI has performed in different market conditions can provide valuable insights into potential future trends. One great way to do this is simply analyzing historical charts.
At TradingSim, for example, you can look back at the S&P GSCI Commodity Index ETF, or any individual futures commodities, and replay these assets to practice your chart eye, looking and observing for trends, patterns, and potential strategies.
Here is an example of the historical chart of GSG, the GSCI ETF, inside TradingSim:
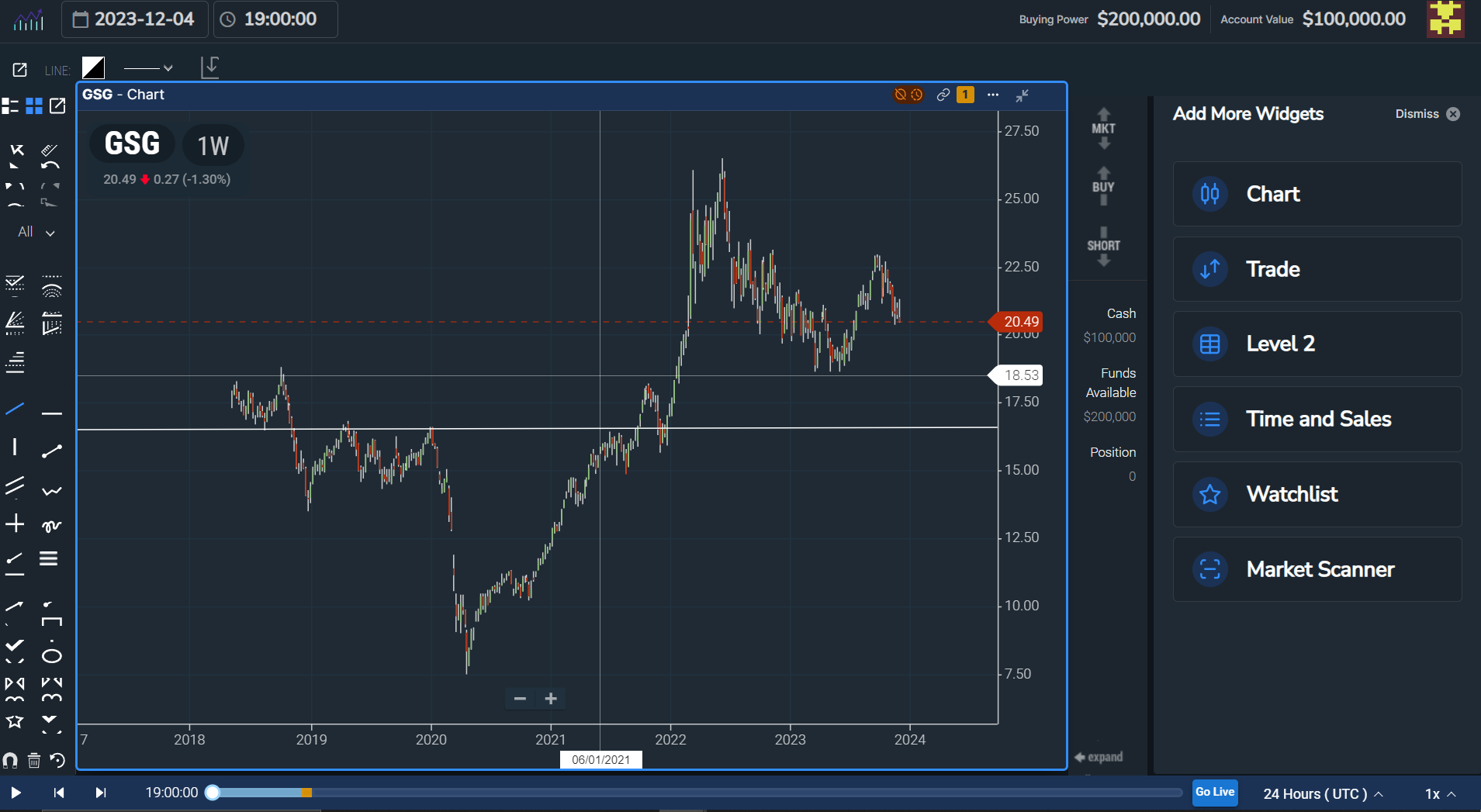
What you'll notice is that GSG, like any other asset has uptrends, downtrends, consolidations, breakouts, and more. We would encourage you to study and analyze the market to find the best opportunistic buy points, just like any other investment.
Economic Factors Impacting Commodity Prices
Several economic factors influence commodity prices, and understanding these variables is essential for successful trading. Factors such as supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and changes in global economic conditions can have a profound impact on commodity markets.
Expert Predictions
Leading experts in the field closely monitor the GSCI and utilize their insights to make predictions about future market movements. While no prediction is foolproof, the cumulative expertise of seasoned analysts might offer valuable guidance to traders. However, here at TradingSim, we believe that making your own decisions based on sound technical analysis often outweighs the importance of expert predictions. Do your research!
Other Major Indices Beyond the GSCI
While the GSCI is a powerful index for commodity trading, there are several others. The Credit Suisse Commodity Benchmark Index, the Dow Jones Commodity Index (DJCI), the Rogers International Commodities Index, and the Bloomberg Commodity Total Return Index are all very popular. Each has its own weighting standard with futures contracts and sectors.
How Can I Buy Commodities?
There are essentially four ways you can gain exposure to commodities in your portfolio.
- Buy the commodity in physical form
- Trade futures contracts for the underlying commodity
- Invest in stocks and companies that do business with the commodity
- Purchase an ETF associated with a commodity or commodity index
Each of these methods for investing in commodities carries its risks and rewards. It will be up to you to decide how you'd like to diversify your portfolio. As with any investment, we recommend you do your homework before purchasing as there may be pitfalls associated with one or the other strategies.
Conclusion
In the world of commodity trading, the Goldman Sachs Commodity Index stands as one of the more respected pillars in the sector. By understanding the components of the S&P GSCI, employing strategic trading strategies, and staying informed about global economic trends, traders can safely navigate adding commodity exposure to their portfolios.
As you embark on your commodity trading journey, remember that successful trading requires a combination of knowledge, strategy, and adaptability. Never put your hard-earned money to work without proper planning and risk management.
Here's to good fills!









 Commodity Futures
Commodity Futures 
