Explore the comprehensive guide to paper trading in futures markets. This article delves into key strategies and tools for effective market simulation, risk management, and portfolio diversification. Ideal for both beginners and experienced traders, it offers insights into leveraging paper trading platforms for financial education and economic forecasting. Discover the secrets to mastering futures trading through simulated environments.
Understanding the Basics of Futures Trading
Futures trading is a form of investing where traders speculate on the future price movements of various commodities, currencies, or financial instruments. It involves buying or selling contracts that represent these assets to make a profit.
Futures Contracts
To understand futures trading, it is important to grasp the concept of a futures contract. A futures contract is an agreement between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price and date in the future. It provides traders with the opportunity to profit from both rising and falling markets.
Granted, for pretty much all modern brokerages, these "contracts" are essentially implied. As in, you're not signing anything on paper when you place a trade. It's built into the process of trading the contracts. Much like you would shares of equities, for example.
Futures Trading 101
In futures trading, participants can take two positions: long or short. Going long means buying a futures contract in anticipation of a price increase, while going short means selling a futures contract in anticipation of a price decrease. Traders can enter and exit positions at any time before the contract's expiration date.
Futures trading offers several advantages, such as leverage, liquidity, and the ability to hedge against price fluctuations. However, it also carries risks, including the potential for substantial losses. Therefore, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of the basics before diving into futures trading.
The Benefits of Paper Trading
Paper trading, also known as simulated trading or virtual trading, is a practice that allows traders to test their strategies and gain experience without risking real money. It involves using a trading simulator that mimics real market conditions and provides users with virtual funds to trade with.
There are several benefits to paper trading.
- Traders can familiarize themselves with a trading platform and its features, such as order types and charting tools.
- It also helps traders gain confidence in their strategies and make necessary adjustments without the fear of incurring financial losses.
- Paper trading allows traders to analyze their trading performance and identify areas for improvement.
- They can track their trades, review the outcomes, and learn from their mistakes. This valuable feedback can help traders refine their strategies and enhance their decision-making skills.
Overall, paper trading is an essential step for aspiring futures traders. It provides a risk-free environment to practice, learn, and develop effective trading strategies before transitioning to live trading with real money. Don't take our word for it, beloved trading psychologist Dr. Brett Steenbarger has this to say about paper trading's benefits:
“Having a plan in the calm of the moment is different from maintaining and acting on the plan once we get punched in the nose!
That doesn’t make simulated trading worthless, however. Even the best boxers practice in the ring away from formal competition to work on their movement, their combinations, etc. Similarly, basketball teams prepare for the next game by scouting the opponent and then practicing against the offense and defense that the opponent are likely to use.
And, of course, where would a Broadway actress or actor be without practicing lines away from the distraction of crowds.
Every performance domain relies on practice away from formal competition to build performance in the heat of the moment.“
Dr. Brett Steenbarger Ph.D.
Key Strategies for Successful Paper Trading
If you want to get the most out of paper trading, you have to go beyond the simple use of simulation. Proper success in paper trading requires study, review, and even backtesting of patterns. Over time, as you observe and replicate certain criteria for market patterns, you'll develop a keen eye for certain strategies.
As you learn and observe, you'll want to develop a playbook based on the criteria you've observed. This playbook can be tweaked and modified as markets evolve.
Developing a Solid Trading Plan
Creating a solid trading plan involves several considerations. Here's a list of how we typically narrow our focus to develop our trading playbook:
-
Goal Definition:
- Clearly define short-term and long-term trading goals. Whether it's capital preservation, consistent profits, or learning specific strategies, having clear objectives is crucial.
-
Risk Tolerance Assessment:
- Evaluate your risk tolerance to determine the acceptable level of risk in each trade. This step sets the stage for effective risk management throughout your paper trading journey.
-
Technical Analysis Techniques:
- Master various technical analysis tools and indicators to identify trends, support/resistance levels, and potential entry/exit points. Utilize charts and historical price data to aid in decision-making.
-
Time Horizon Analysis:
- Define the time horizon for trades, whether they are day trades, swing trades, or long-term investments. The trading plan should reflect your chosen timeframes and associated strategies.
-
Entry and Exit Criteria:
- Clearly outline criteria for entering and exiting trades. This includes technical indicators, fundamental factors, and any specific signals that trigger trade executions or closures.
-
Adaptability to Market Conditions:
- Develop strategies that are adaptable to changing market conditions. This includes recognizing trends, sideways markets, and volatile periods, and adjusting trading approaches accordingly
Navigating Economic Forecasting in Simulated Environments
Understanding economic headwinds or tailwinds can make or break a trading strategy, especially with futures trading. As you consider the commodities or assets you want to trade, economic factors may influence the direction of your trade.
For example, the price of soy, corn, or oil could be impacted by economic factors in farming and drilling. One tool you might use in paper trading is historical news and economic data to compare with the price fluctuations of commodities during those time periods.
Here are some other considerations you might make when considering economic forecasting on simulated futures trading:
Global Events and Market Sentiment
Monitor global events and market sentiment to anticipate how they might influence asset prices. This includes geopolitical developments, economic policy changes, and investor sentiment.
Macroeconomic Awareness
Stay abreast of macroeconomic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and interest rates, and understand their potential impact on different futures commodities.
Mastering key strategies in paper trading involves a blend of planning, execution, and adaptability. Traders who develop a solid trading plan, implement effective market strategies, and pay attention to economic forecasting will be better positioned to transition from simulated environments to live trading with confidence and competence.
Tools and Platforms for Paper Trading
Choosing the right paper trading platform is an important step toward mastering futures trading. Not every paper trading platform is created equally. Some brokers offer a clunky option for paper trading based on their own platform, while others build from scratch with the sole purpose of paper trading in mind.
For more information, we've done a comprehensive review of our top simulators here.
Overview of Popular Paper Trading Platforms
TradingSim:
Packed with realistic trading and review features, it is the only paper trading app dedicated solely to market simulation. With custom screeners, a customizable interface, and other amazing features, Tradingsim is a must for market replay.
Thinkorswim:
A comprehensive platform by TD Ameritrade, Thinkorswim offers advanced charting tools, technical analysis features, and a sophisticated interface based on its flagship trading platform. It caters to both novice traders and seasoned professionals. Data feeds can be a little unreliable.
DAS Trader Pro:
DAS is a simple, Windows-based trading platform geared for active retail and professional day traders. As part of your subscription with DAS, you have the option to pay extra for simulated trading. This will allow you to download a single ticker symbol and replay it for a date of your choice.
Interactive Brokers (IBKR) Paper Trading:
Interactive Brokers provides a fairly robust paper trading platform. It mirrors the functionalities of the live trading environment and caters to traders with diverse strategies.
What Features Should a Paper Trading Application Have?
A great paper trading application will have a dynamic set of features like charting, customizability, watchlist, scanners, hotkeys, and more. Here are at least 6 items that your futures paper trading application should have:
-
Real-time Market Data:
- Access to real-time market data allows traders to experience the dynamics of live markets. This feature enhances the authenticity of the paper trading experience.
-
Watchlists and Scanners:
- Paper trading platforms should offer the ability to create watchlists and customized screens based on historical charts.
-
Performance Tracking:
- Virtual trading accounts come equipped with performance-tracking tools. Traders can analyze their trades, assess strategies, and identify areas for improvement.
-
Charting and Technical Analysis:
- Comprehensive charting tools and technical analysis features allow traders to apply diverse strategies and indicators in a simulated setting.
-
Order Execution Montage:
- Virtual trading accounts simulate the order execution process, allowing traders to understand the mechanics of placing trades, setting stop-loss orders, and executing various order types.
-
Level 2 and Time and Sales:
- Seeing order flow is crucial to day trading. Any simulator worth its weight will offer realistic, historical time and sales data along with level 2 bid and ask prices.

Four Technical Strategies for Futures Paper Trading
Strategy 1: Trend Following
Trend following is a popular futures trading strategy that aims to capitalize on the momentum of price movements. It involves identifying and trading in the direction of established trends, whether bullish (upward) or bearish (downward).
To implement the trend-following strategy, traders use technical indicators, such as moving averages, to identify the direction of the trend. Enter long positions when the price is trending upwards and short positions when the price is trending downwards.
It's important to note that not all trends persist. If your strategy is intermediate to longer-term, you'll likely do better with a trend-following strategy as the overall market or underlying economic conditions warrant a patient approach.
As the market typically acts in stages, most proficient traders take long trades as a commodity enters a stage 2 markup phase or short trades as it enters a stage 4 markdown.
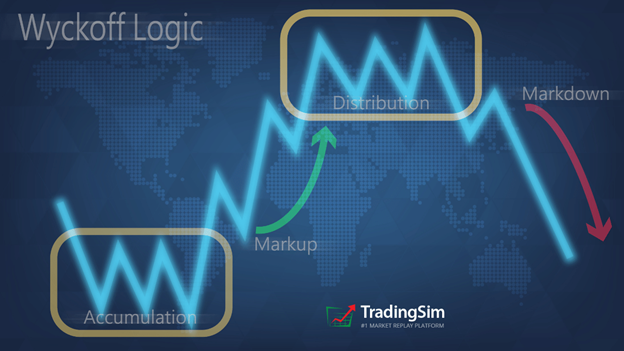
Strategy 2: Breakout Trading
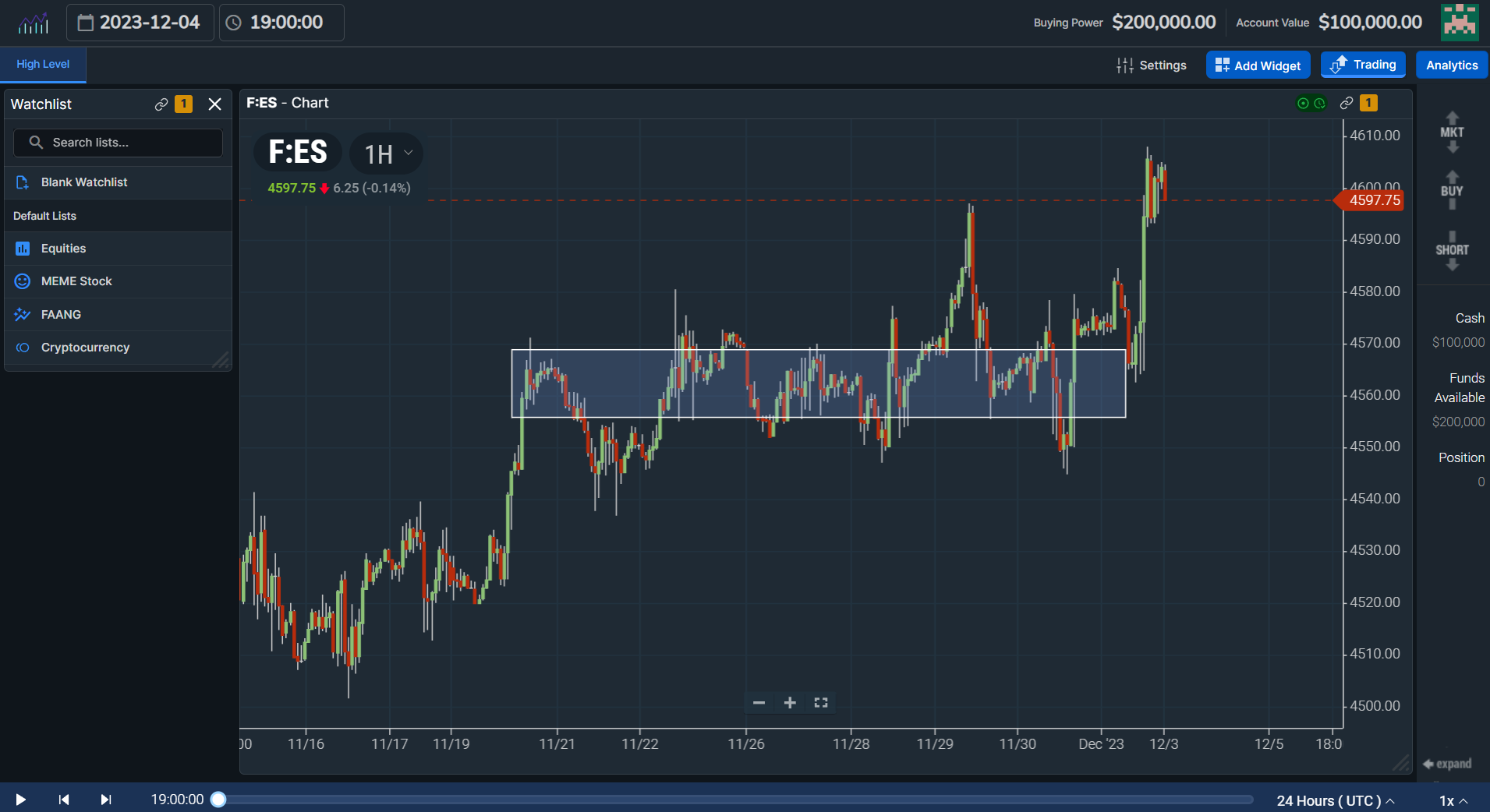
Breakout trading is a strategy that aims to capture significant price movements that occur when an asset breaks out of a trading range or a specific price level. It involves entering a trade as soon as the price breaks above resistance or below support.
To identify potential breakout opportunities, traders can use technical analysis tools, such as trendlines, support and resistance levels, and chart patterns. Set entry orders above the resistance level or below the support level to automatically enter a trade when the breakout occurs.
Breakout trading requires careful risk management, as false breakouts can lead to losses. Traders can use stop-loss orders to limit their potential downside and take-profit orders to lock in profits when the price reaches a certain target.
Below is an example of a breakout trendline for GSG on a weekly chart:
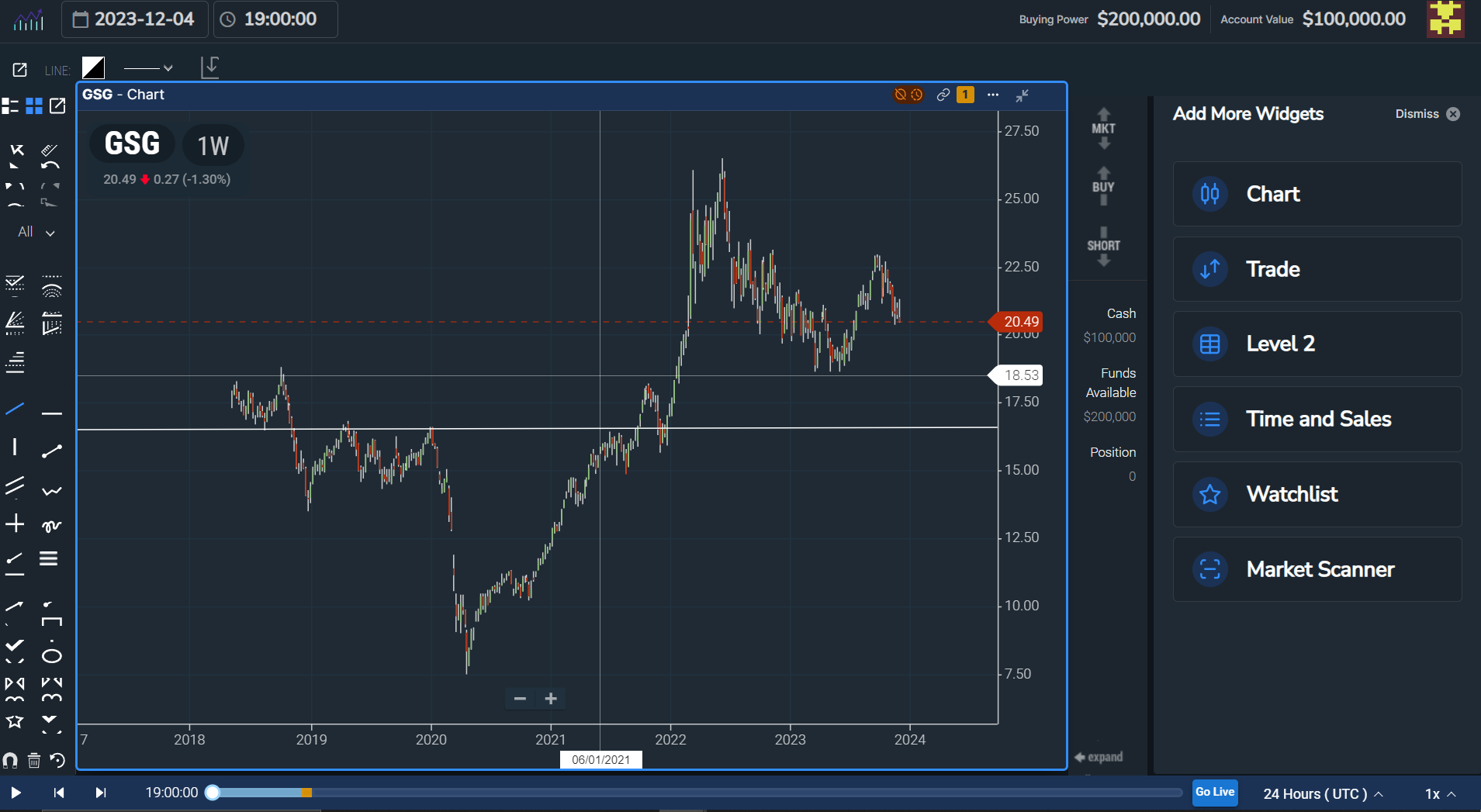
Strategy 3: Mean Reversion Trading
Mean reversion trading is a strategy based on the principle that prices tend to revert to their average or mean over time. It involves identifying overbought or oversold conditions and taking positions that anticipate a reversal in price.
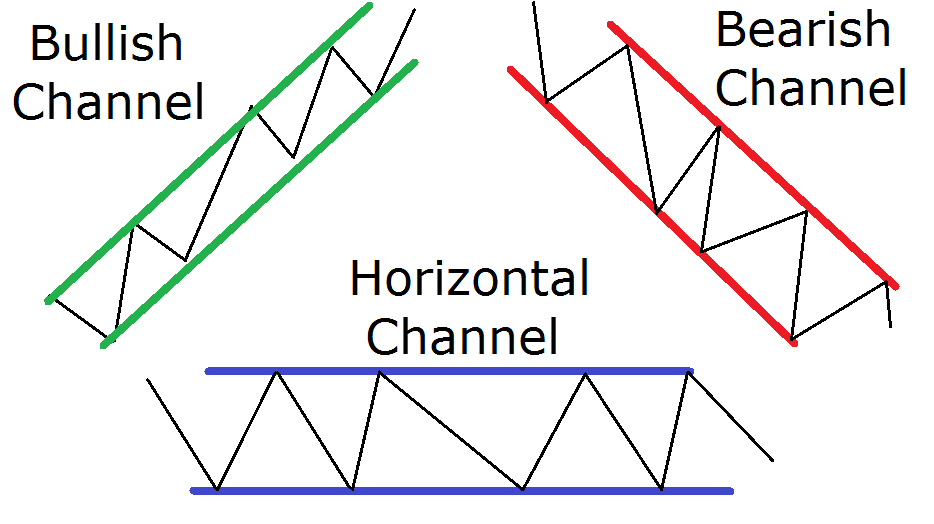
To implement the mean reversion strategy, traders can use technical indicators, such as oscillators or Bollinger Bands, to identify extreme price levels. Enter trades when the price is stretched too far from its average and expect it to revert towards the mean.
Mean reversion trading requires discipline and patience, as it may take time for prices to revert. Traders must also be mindful of potential trend continuation and use stop-loss orders to manage their risk.
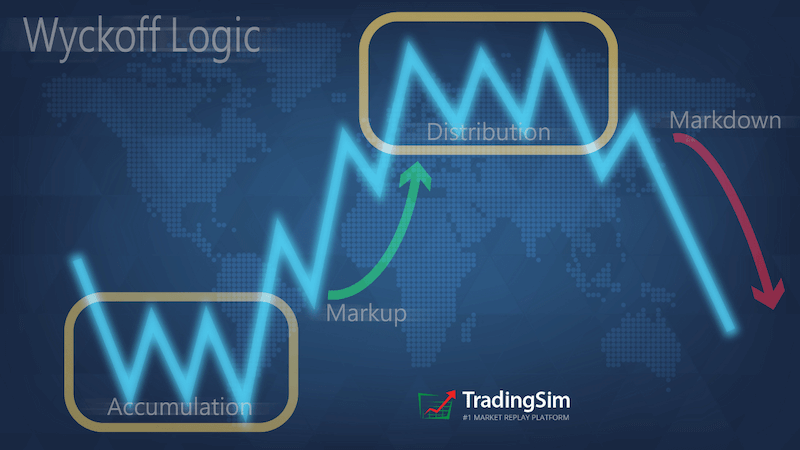
Strategy 4: Liquidity Zones
Liquidity zones are areas on a futures chart that show you where big-money players are either accumulating or distributing their contracts. Typically prices will congregate in these areas as long as there is supply or demand present. However, once supply is exhausted, or vice-versa, the price will move away from the area in the direction of least resistance.
When a futures contract is under accumulation, it will often remain in an area long enough for institutions to accumulate contracts. Once enough contracts have been bought, the price is marked up. Hence, you see how price moves higher out of these liquidity zones.
In contrast, when the price of a commodity has gotten too extended, you are likely to see the distribution of those contracts that were accumulated at much lower prices. The result is “ease of movement” back to the liquidity zones that supported the asset before.
To execute these trades, you identify the area of liquidity and take your position based on which direction the tape wants to move. If the tape is heavy and distribution has occurred in the liquidity zone, you'd take a short position. For accumulation, you'd go long.
Challenges and Pitfalls in Paper Trading
One of the biggest challenges that any trader will face is emotional/psychological maturity. Too often traders fail because they can't handle the emotional swings associated with profits and losses. This eventually takes its toll and burns most new traders out.
In simulated trading, you have the benefit of trading with virtual money so that your profit/loss swings aren't as difficult to stomach. However, this can be a catch-22 for the trader who isn't serious about learning. It could either desensitize you to the losses and result in massive risk management problems or ill-prepare you for the real cuts in the market.
Either way, paper trading has its purpose in identifying positive correlations between patterns and price action in markets. Stay focused on using the tool as a means to an end, and be aware of the emotional realities that will come with trading real money.
Conclusion
Paper trading futures can be a great way to prepare yourself for the real markets. It's also a great tool for experienced traders to test out new strategies. As we've discussed, there are several factors to consider when choosing a paper trading application, like customizability, watchlist, live order montage, and historical, realistic data feeds.
We can't emphasize the importance of constant learning. No trader is above learning something new, and even successful traders understand how powerful review and observation can be. Futures simulation trading platforms allow you to do this.
Here at TradingSim, we pride ourselves on developing the only standalone futures, equities, and crypto simulation platform on the net. Our product allows you to replay markets from years in the past, at any time of day. We hope you'll take advantage of the platform and give it a test drive.











 Day Trading Platform
Day Trading Platform 
